RollbackSynchronizer
Manages state during the network rollback loop by hooking into NetworkRollback events. Simulates nodes as required during rollback.
To read more on best practices, see Rollback caveats.
Configuring state and input
To use RollbackSynchronizer, add it as a child to the target node, specify the root node, and configure which properties to manage:
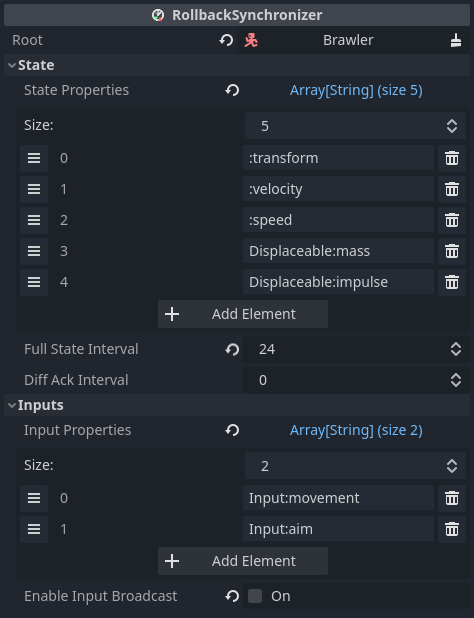
Root specifies the root node for resolving state and input properties. Best practice dictates to add RollbackSynchronizer under its target, so Root will most often be the RollbackSynchronizer's parent node.
State properties are recorded for each tick and restored during rollback. For state, the server is the ultimate authority. Make sure that nodes containing state properties are owned by the server.
Full state interval specifies how many ticks to wait between full states. If diff states are enabled, full states are only sent at specific intervals, to make sure that peers always have the correct state data. Only considered if diff states are enabled.
Diff ack interval specifies how many ticks to wait between acknowledging diff states. Setting this to lower non-zero values may result in more bandwidth savings on non-changing properties, but this can be outweighed by the increased number of ack messages. Only considered if diff states are enabled.
See diff states for more on how the above two settings are used.
Input properties are gathered for each player and sent to the server to use for simulation. Make sure that nodes containing input properties are owned by their respective players.
See Property paths on how to specify properties.
Enable input broadcast toggles whether input properties are broadcast to all peers, or only to the server. The default is true to support legacy behaviour. It is recommended to turn this off to lower bandwidth and lessen the attack surface for cheating.
Warning
It is not recommended to have both state and input properties on the same node. Since nodes with state belong to the server, and nodes with input belong to the player, it is difficult to separate ownership on the same node.
Writing rollback-aware scripts
During setup, RollbackSynchronizer finds all the rollback-aware nodes under the specified root. During rollback, it will call all the rollback-aware nodes to simulate new state.
To learn about rollback-awareness, see NetworkRollback.
In short, implement _rollback_tick in your scripts:
extends CharacterBody3D
@export var speed = 4.0
@export var input: PlayerInput
func _rollback_tick(delta, tick, is_fresh):
velocity = input.movement.normalized() * speed
velocity *= NetworkTime.physics_factor
move_and_slide()
velocity /= NetworkTime.physics_factor
Note the usage of physics_factor - this is explained in Rollback caveats.
Single fire events
The first time a rollback tick is processed, the is_fresh parameter is set to
true. This can be used to trigger animations or sounds without them being
repeated each rollback event.
For example to improve the client side experience a spell or weapon can play its activating sounds and animation immediately and then proceed to complete the action once server confirmation is received.
Changing configuration
RollbackSynchronizer has to do some setup work whenever the state or the input properties change.
By default, this work is done upon instantiation. If you need to change state
or input properties during runtime, make sure to call process_settings(),
otherwise RollbackSynchronizer won't apply the changes.
While changing configuration after instantiation is possible, it is not recommended. You may get away with it if the configuration change happens in a few ticks after instantiation. For longer periods, experiment at your own risk.
Changing ownership
The setup work above is also needed whenever the multiplayer authority changes of any of the nodes that have a state- or input property.
Changing authority during gameplay is supported. Make sure to call
process_authority() on all peers at the same time, to ensure they're on sync
about ownership.
This method is called automatically during instantiation and whenever
process_settings() is called.
When only multiplayer authority changes, call process_authority(). When the
configured state- or input properties change ( i.e. different properties need
to be synced ), call process_settings().
Diff states
When diff states are enabled in the rollback settings, netfox will attempt to save bandwidth by only sending state properties that have changed.
These changes are always based on a tick that the receiving peer has confirmed it already has. Basically we don't want to send changes compared to a tick that the peer has no knowledge about.
Peers notify the host of which ticks they know about by acknowledging ( or ack'ing ) ticks. This acknowledging has two flavors.
The first flavor is full states. These states contain all the state data, regardless of what changed and what has stayed the same. These ensure that peers have all the state data for a given tick. Once a full state is received, the receiving peer acknowledges that tick over a reliable channel.
The second flavor is diff states. Peers may also acknowledge ticks after receiving a diff state, meaning that they have reconstructed the given state from a known earlier state and the diff state received. These are acknowledged over an unreliable channel. By using an unreliable channel, we can acknowledge diff states more often without causing any hiccups in network traffic.
When diff states are disabled, netfox will always send full state data for all ticks.